1. Credit 데이터셋
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
credit_df = pd.read_csv('/content/drive/MyDrive/KDT v2/머신러닝과 딥러닝/ data/credit.csv')
credit_df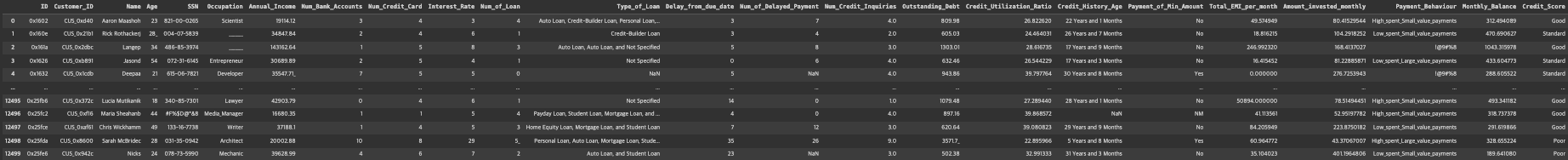
# 컬럼의 최대치를 50으로 설정
pd.set_option('display.max_columns', 50)
# 정보 확인
credit_df.info()
# # Column Non-Null Count Dtype
# --- ------ -------------- -----
# 0 ID 12500 non-null object
# 1 Customer_ID 12500 non-null object
# 2 Name 11273 non-null object
# 3 Age 12500 non-null object
# 4 SSN 12500 non-null object
# 5 Occupation 12500 non-null object
# 6 Annual_Income 12500 non-null object
# 7 Num_Bank_Accounts 12500 non-null int64
# 8 Num_Credit_Card 12500 non-null int64
# 9 Interest_Rate 12500 non-null int64
# 10 Num_of_Loan 12500 non-null object
# 11 Type_of_Loan 11074 non-null object
# 12 Delay_from_due_date 12500 non-null int64
# 13 Num_of_Delayed_Payment 11657 non-null object
# 14 Num_Credit_Inquiries 12264 non-null float64
# 15 Outstanding_Debt 12500 non-null object
# 16 Credit_Utilization_Ratio 12500 non-null float64
# 17 Credit_History_Age 11387 non-null object
# 18 Payment_of_Min_Amount 12500 non-null object
# 19 Total_EMI_per_month 12500 non-null float64
# 20 Amount_invested_monthly 11935 non-null object
# 21 Payment_Behaviour 12500 non-null object
# 22 Monthly_Balance 12366 non-null float64
# 23 Credit_Score 12500 non-null object한/영 변환
| English | 한글 |
|---|---|
| ID | 고유 식별자 |
| Customer_ID | 고객 ID |
| Name | 이름 |
| Age | 나이 |
| SSN | 주민등록번호 |
| Occupation | 직업 |
| Annual_Income | 연간 소득 |
| Num_Bank_Accounts | 은행 계좌 수 |
| Num_Credit_Card | 신용 카드 수 |
| Interest_Rate | 이자율 |
| Num_of_Loan | 대출 수 |
| Type_of_Loan | 대출 유형 |
| Delay_from_due_date | 마감일로부터 연체 기간 |
| Num_of_Delayed_Payment | 연체된 결제 수 |
| Num_Credit_Inquiries | 신용조회 수 |
| Outstanding_Debt | 미상환 잔금 |
| Credit_Utilization_Ratio | 신용카드 사용률 |
| Credit_History_Age | 카드 사용 기간 |
| Payment_of_Min_Amount | 리볼빙 여부 |
| Total_EMI_per_month | 월별 총 지출 금액 |
| Amount_invested_monthly | 매월 투자 금액 |
| Payment_Behaviour | 지불 행동 |
| Monthly_Balance | 월별 잔고 |
| Credit_Score | 신용 점수 |
credit_df.drop({'ID', 'Customer_ID', 'Name', 'SSN'}, axis=1, inplace=True)
credit_df['Credit_Score'].value_counts()
# 결과 =>
# Standard 6943
# Poor 3582
# Good 1975
# Name: Credit_Score, dtype: int64
credit_df['Credit_Score'] = credit_df['Credit_Score'].replace({'Poor':0, 'Standard':1, 'Good':2})
credit_df.describe()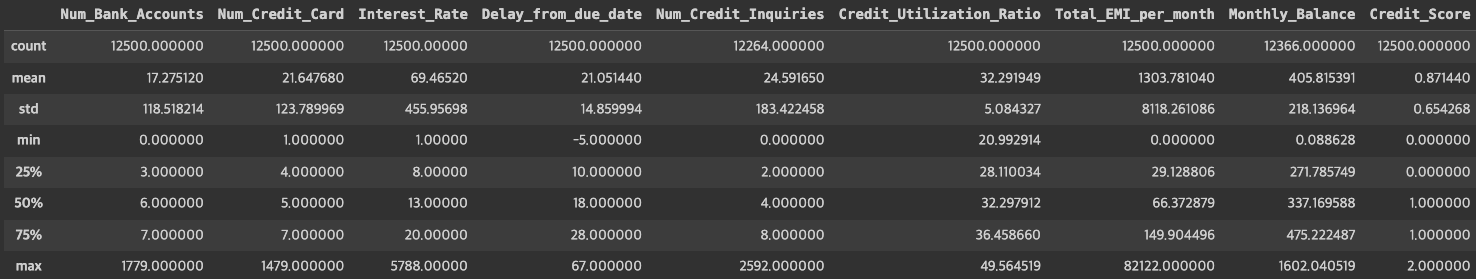
sns.barplot(x='Payment_of_Min_Amount', y='Credit_Score', data=credit_df)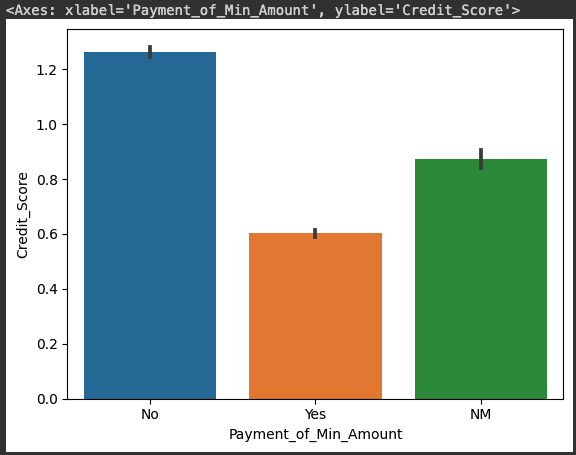
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 5))
sns.barplot(x='Occupation', y='Credit_Score', data=credit_df)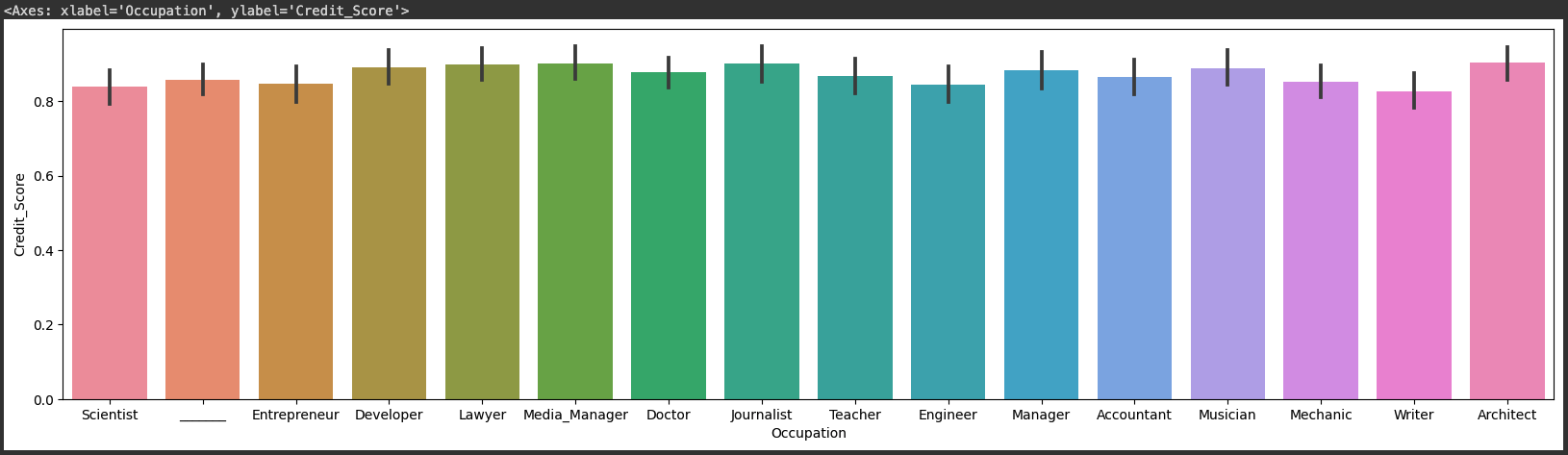
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
sns.heatmap(credit_df.corr(), cmap='coolwarm', vmin=-1, vmax=1, annot=True)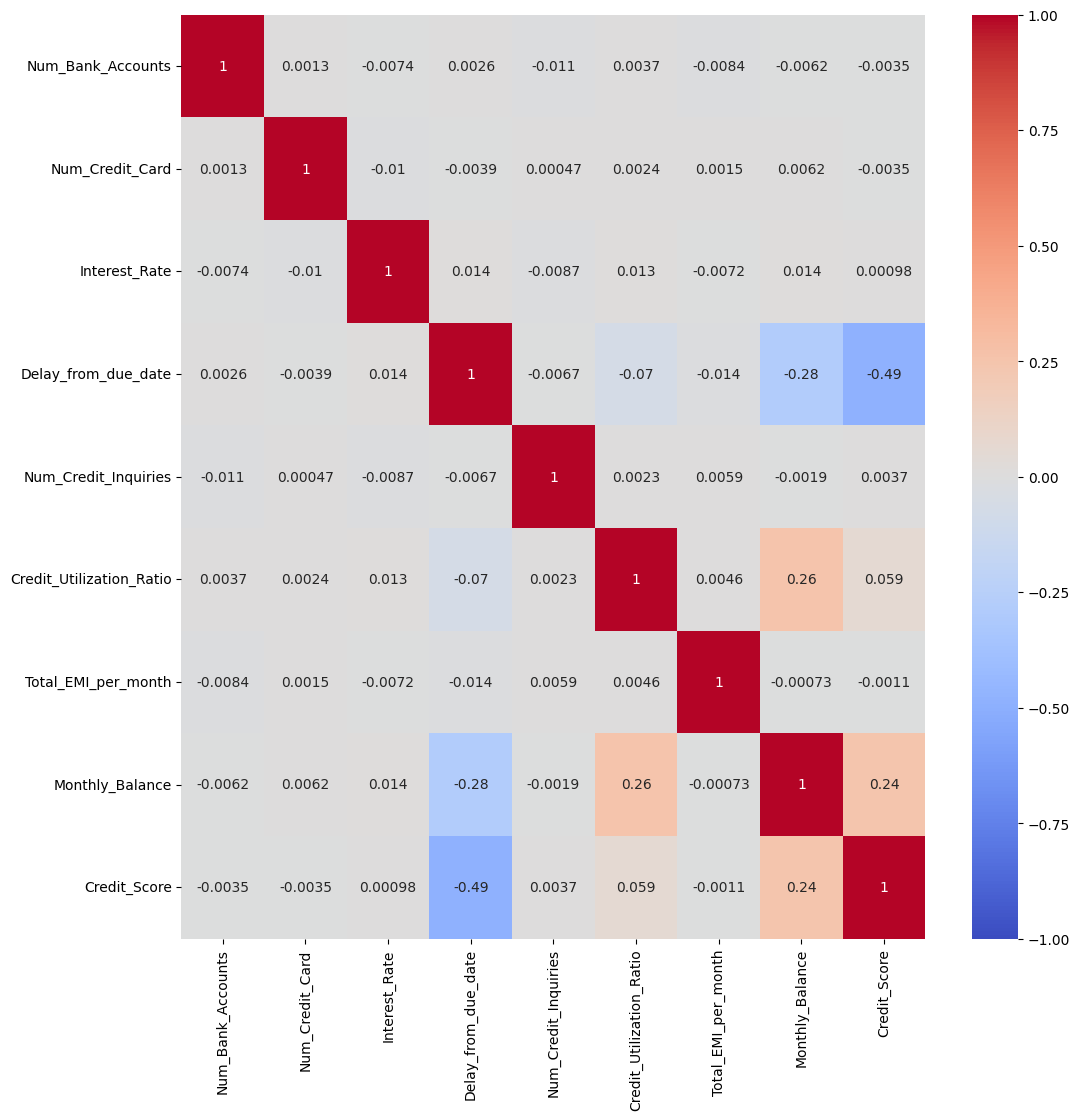
for i in credit_df.columns:
if credit_df[i].dtype == 'O':
print(i)
# 결과값 =>
# Age
# Occupation
# Annual_Income
# Num_of_Loan
# Type_of_Loan
# Num_of_Delayed_Payment
# Outstanding_Debt
# Credit_History_Age
# Payment_of_Min_Amount
# Amount_invested_monthly
# Payment_Behaviour
# _를 제거
for i in ['Age', 'Annual_Income', 'Num_of_Loan', 'Num_of_Delayed_Payment', 'Outstanding_Debt', 'Amount_invested_monthly']:
credit_df[i] = pd.to_numeric(credit_df[i].str.replace('_', ''))
credit_df['Credit_History_Age'] = credit_df['Credit_History_Age'].str.replace(' Months', '')
credit_df['Credit_History_Age'] = pd.to_numeric(credit_df['Credit_History_Age'].str.split(' Years and ', expand=True)[0]) * 12 + pd.to_numeric(credit_df['Credit_History_Age'].str.split(' Years and ', expand=True)[1])
credit_df = credit_df[credit_df['Age'] >= 0]
sns.boxplot(y=credit_df['Age'])

credit_df = credit_df[credit_df['Age'] < 110]
credit_df = credit_df[credit_df['Num_Bank_Accounts'] <= 10]
credit_df=credit_df[credit_df['Num_Credit_Card']<=20]
credit_df = credit_df[credit_df['Interest_Rate'] <= 40]
credit_df = credit_df[(credit_df['Num_of_Loan'] <= 10) & (credit_df['Num_of_Loan'] >= 0)]
credit_df = credit_df[credit_df['Delay_from_due_date'] >= 0]
credit_df = credit_df[(credit_df['Num_of_Delayed_Payment'] <= 30) & (credit_df['Num_of_Delayed_Payment'] >= 0)]
credit_df['Num_Credit_Inquiries'] = credit_df['Num_Credit_Inquiries'].fillna(0)
sns.displot(credit_df['Credit_History_Age'])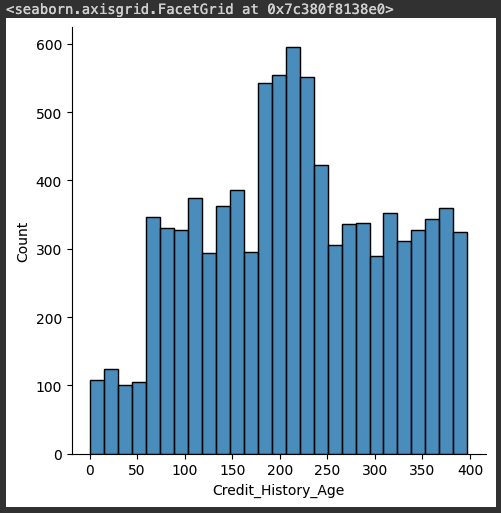
sns.displot(credit_df['Amount_invested_monthly'])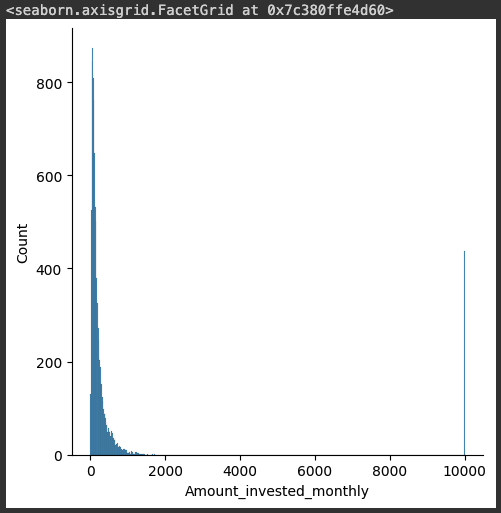
sns.displot(credit_df['Monthly_Balance'])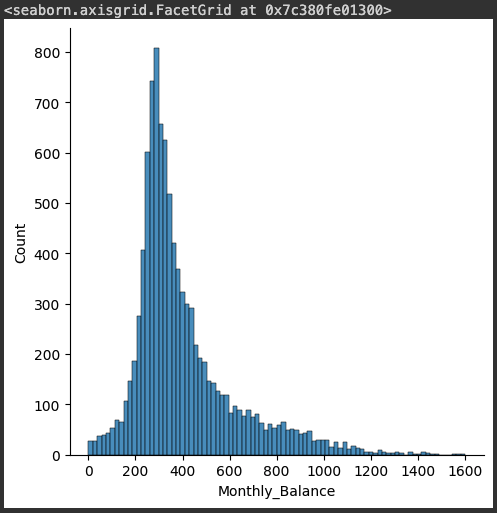
credit_df = credit_df.fillna(credit_df.median())
credit_df.isna().mean()
# 결과값 =>
# Age 0.000000
# Occupation 0.000000
# Annual_Income 0.000000
# Num_Bank_Accounts 0.000000
# Num_Credit_Card 0.000000
# Interest_Rate 0.000000
# Num_of_Loan 0.000000
# Type_of_Loan 0.111056
# Delay_from_due_date 0.000000
# Num_of_Delayed_Payment 0.000000
# Num_Credit_Inquiries 0.000000
# Outstanding_Debt 0.000000
# Credit_Utilization_Ratio 0.000000
# Credit_History_Age 0.000000
# Payment_of_Min_Amount 0.000000
# Total_EMI_per_month 0.000000
# Amount_invested_monthly 0.000000
# Payment_Behaviour 0.000000
# Monthly_Balance 0.000000
# Credit_Score 0.000000
credit_df['Type_of_Loan'] = credit_df['Type_of_Loan'].str.replace('and ', '')
# No Loan이라는 필드를 생성
credit_df['Type_of_Loan'] = credit_df['Type_of_Loan'].fillna('No Loan')
type_list = set(credit_df['Type_of_Loan'].str.split(', ').sum())
type_list
# 결과값 =>
# {'Auto Loan',
# 'Credit-Builder Loan',
# 'Debt Consolidation Loan',
# 'Home Equity Loan',
# 'Mortgage Loan',
# 'No Loan',
# 'Not Specified',
# 'Payday Loan',
# 'Personal Loan',
# 'Student Loan'}
for i in type_list:
credit_df[i] = credit_df['Type_of_Loan'].apply(lambda x: 1 if i in x else 0)
credit_df.drop('Type_of_Loan', axis=1, inplace=True)
credit_df['Occupation'].value_counts()
# 결과값 =>
# _______ 674
# Lawyer 664
# Mechanic 646
# Scientist 640
# Engineer 640
# Architect 633
# Teacher 624
# Developer 621
# Entrepreneur 620
# Media_Manager 616
# Accountant 611
# Doctor 608
# Musician 607
# Journalist 606
# Manager 602
# Writer 592
# Name: Occupation, dtype: int64
credit_df['Occupation'] = credit_df['Occupation'].replace('_______', 'Unknown')
credit_df['Payment_Behaviour'].value_counts()
# 결과값 =>
# Low_spent_Small_value_payments 2506
# High_spent_Medium_value_payments 1794
# High_spent_Large_value_payments 1453
# Low_spent_Medium_value_payments 1376
# High_spent_Small_value_payments 1136
# Low_spent_Large_value_payments 995
# !@9#%8 744
# Name: Payment_Behaviour, dtype: int64
credit_df['Payment_Behaviour'] = credit_df['Payment_Behaviour'].str.replace('!@9#%8', 'Unknown')
credit_df = pd.get_dummies(credit_df, columns={'Occupation', 'Payment_of_Min_Amount', 'Payment_Behaviour'})
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(credit_df.drop('Credit_Score', axis=1), credit_df["Credit_Score"], test_size=0.2, random_state=2023)
X_train.shape, y_train.shape
# 결과값 => ((8003, 51), (8003,))
X_test.shape, y_test.shape
# 결과값 => ((2001, 51), (2001,))
lightGBM(LGBM)
- Microsoft에서 개발한 Gradient Boosting Framework
- 리프 중심 히스토그램 기반 알고리즘
- GBM(Gradient Boosting Model) : 모델1을 통해 y를 예측하고, 모델2에 데이터를 넣어 y를 예측하고, 모델3에 넣어 y를 예측하는 방식
- 작은 데이터셋에서도 높은 성능을 보이며, 특히 대용량 데이터셋에서 다른 Gradient Boosting 알고리즘보다 빠르게 학습.
- 메모리 사용량이 상대적으로 적은편
- 적은 데이터셋을 사용할 경우 과적합 가능성이 매우 큼(일반적으로 데이터가 10,000개 이상은 사용 해야함)
- 조기 중단(early stopping)을 지원
리프 중심 히스토그램 기반 알고리즘
- 트리를 균형적으로 분할하는 것이 아니라, 최대한 불균형하게 분할
- 특성들의 분포를 히스토그램으로 나타내고, 해당 히스토그램을 이용하여 빠르게 후보 분할 기준을 선택
- 후보 분할 기준 중에서 최적의 분할 기준을 선택하기 위해, 데이터 포인트들을 히스토그램에 올바르게 배치하고, 이용하여 최적의 분할 기준을 선택
from lightgbm import LGBMClassifier
base_model = LGBMClassifier(random_state=2023)
base_model.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = base_model.predict(X_test)from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report, roc_auc_score
accuracy_score(y_test, pred)
# 결과값 => 0.7251374312843578
confusion_matrix(y_test, pred)
# 결과값 =>
# array([[409, 144, 25],
# [154, 855, 108],
# [ 4, 115, 187]])print(classification_report(y_test, pred))
# 결과값 =>
# precision recall f1-score support
#
# 0 0.72 0.71 0.71 578
# 1 0.77 0.77 0.77 1117
# 2 0.58 0.61 0.60 306
#
# accuracy 0.73 2001
# macro avg 0.69 0.69 0.69 2001
# weighted avg 0.73 0.73 0.73 2001
proba = base_model.predict_proba(X_test)
# 클래스가 3개 이상이므로 그냥 (y_test, proba)만 적으면 에러가 발생한다.
# 그러므로 multi_class='ovr'옵션을 추가하여 값을 추출한다.
roc_auc_score(y_test, proba, multi_class='ovr')
# 결과값 => 0.8932634160489487
'Study > 머신러닝과 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [머신러닝과 딥러닝] 12.KMeans (1) | 2024.01.08 |
|---|---|
| [머신러닝과 딥러닝] 11. 다양한 모델 적용 (0) | 2024.01.08 |
| [머신러닝과 딥러닝] 9. 랜덤 포레스트 (0) | 2024.01.03 |
| [머신러닝과 딥러닝] 8. 서포트 백터 머신 (0) | 2024.01.02 |
| [머신러닝과 딥러닝] 7. 로지스틱 회귀 (0) | 2024.01.02 |
